Friday, December 16, 2022
useful pics
Thursday, January 13, 2022
BEING SINGLE SUCKS!
KNOWING WHAT YOU WANT IN LIFE
LEAVING THE VILLAGE
Sunday, June 20, 2021
12 Surprising Facts About Nursing You Might Not Know!
If you’re in the nursing industry as a registered nurse, nurse practitioner, nurse’s assistant or own a nurse staffing agency, you’re aware of what goes on in the field of nursing. For example, you probably know that there is a nursing shortage in the United States, the average salary of a nurse or how large the profession is as a whole
Nurses might be the blood and beating heart of a
hospital, but you might not know as much as you think though. Test your
knowledge with these unique facts and statistics about nursing that might leave
you shocked and surprised.
1. It’s old.
We have to start off our list of nursing fun facts with
some history. The first record of nurses dates all the back to 300 A.D. in the
Roman Empire. They worked in hospitals that eventually became relatively
developed. It wasn’t until the Middle Ages that nursing had many advances
and became more widespread.
2. Florence Nightingale shaped the profession
and healthcare.
One of the most famous nurses was a British woman,
Florence Nightingale. Not only did she save many soldiers lives, she changed
the way nurses were educated and how nursing as a profession was viewed by
society.
Specifically, she changed the way hospitals were
sanitized, how food was prepared and served and how to treat wounded patients
to prevent the spread of infection. This interesting fact about nursing is an
important one that evolved the industry.
3. Bellevue Hospital School of Nursing was
the first nursing school.
This nursing school started in 1873 based on the
principles of Florence Nightingale. Located in New York City, this nursing
school offered a one year program. Shortly after Bellevue Hospital School of
Nursing opened, New England Hospital for Women and Massachusetts General
Hospital opened nursing schools as well.
4. Nurses walk a 5k every shift.
On average, nurses walk four to five
miles every shift 12-hour shift they
work. That’s a lot of walking.
Compare that to the average person who only walks about
2.5 miles on average. Nurses walk double the distance every shift than the
average population does daily. This interesting fact about nursing proves why
nurses need a comfortable pair of shoes!
5. Half of the students studying a health
care related topic are in nursing.
Nursing students represent about 50 percent of
individuals studying some form of health care at a higher education level. This
is a direct reflection of the industry as a whole. In order for healthcare to
operate smoothly as a whole, there needs to be a large number of nurses.
This is beneficial for students going through nursing
school and nursing programs because of the large, supportive peer group.
6. Top jobs of 2018.
According to U.S. News and World Reports three of the 25
best jobs of 2018 are types of nurses. Registered nurses are ranked #18, nurse
anesthetists are #22 and nurse practitioners are all the way up at #4.
If you own a nurse staffing agency, you’re services will
continue to be of value to nurses and facilities that need additional nurses.
This is even a fact about nursing that you can use as a marketing point for
your staffing services.
7. Mary Eliza Mahoney was the first African
American RN.
For 15 years, Mary Eliza Mahoney worked in a hospital
before actually becoming a nurse. She started as a cook, then became a janitor
and did laundry. She was an unofficial nurses aid, which is what impacted her
to to become a registered nurse.
She was only one of the three nurses to make it through
the New England Hospital training program. Later, she went on to to co-find the
National Association of Colored Graduate Nurses.
8. There are three million nurses in the U.S.
The U.S. Bureau of
Labor Statistics reported
that there were about three million nurses as of 2016. This numerical fact
about nursing is shocking because the population of Jamaica is roughly the same
as the amount of nurses in the United States. To put this into perspective,
there are roughly as many nurses as people living in Los Angeles.
On a more global scale, there are over 19 million nurses
in the world.
9. The field of nursing will continue
growing.
Similar to the nursing fact about top jobs, the field of
nursing will continue to grow for the next decade. It is estimated the by 2026,
there will be a 15 percent growth of employment of nurses.
If you own a nurse staffing agency, this means you have
the opportunity to grow your business as well.
10. Nurses aren’t just in hospitals.
This nursing fact isn’t groundbreaking, but contrary to
popular belief, only 41 percent of registered nurses work in hospitals. Here’s
the total breakdown of where nurses work:
·
14%
skilled nursing home or assisted living facility
·
11%
home health care
·
4%
private practice
·
4%
community heathcare centers
·
4% VA
hospitals
·
22%
other
11. National nurses week is May 6 to May 12.
This annual week to honor nurses has been celebrated for
over 40 years. It even ends on the day that Florence Nightingale was born!
National nurses week was established to acknowledge the
challenging job of being a nurse and to let nurses know that their hard work is
recognized and appreciated. Learn more about
this year’s theme and events here.
12. Many nurses are employed through a
staffing agency.
Nurses work through a nurse staffing agency to help them
find jobs and new opportunities. If you own a nurse staffing agency, it’s
important to have the funding to can keep up with the rising demand for nurses.
Learn how nursing staffing financing and invoice factoring for nurse staffing agencies can help your staffing company grow!
Friday, January 29, 2021
MYTHOMANIA
MYTHOMANIA
The compulsive urge to lie about matters big and small or pathological tendency to exaggerate, regardless of the situation also known as pathological lying or habitual lying.
People with pathological lying don’t on lie for particular reason, sometimes they lie for absolutely no reason at all! Though the cause is not known, may result from a mental condition, such as antisocial personality disorder, while others appear to have no medical reason for the behavior. Some evidence from 2007Trusted Source suggests that issues affecting the central nervous system may predispose someone to pathological lying.
This can make it frustrating or hard to know what to do if you believe you’ve met one. The following are some of the scientifically recognized Trusted Source traits and characteristics of pathological liars.
1. Their lies seem to have no clear benefit
2. The stories they tell are usually dramatic, complicated and detailed
3. They usually portray themselves as the hero or victim
4. They sometimes seem to believe the lies they tell
How do we cope with pathological liars?
Since the lying appears to be pointless, It can test the trust in any relationship and make it hard to even have a simple conversation with the person. Here are a few pointers to help you handle a conversation with a pathological liar:
· don’t loose your temper
· expect denial
· be supportive
· don’t engage them
· remember its not about you
· suggest medical help
Saturday, January 23, 2021
Alzheimer's vs Dementia
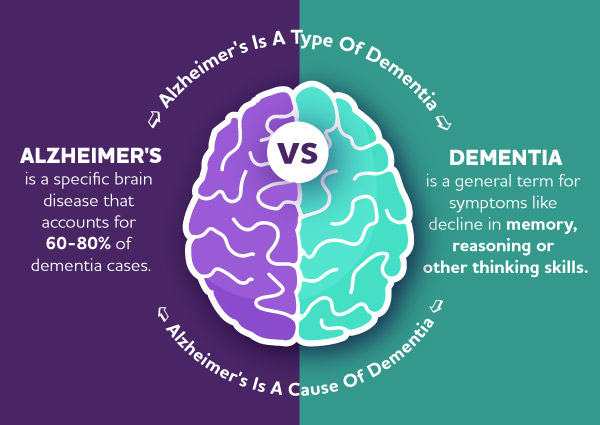
Alzheimer's vs Dementia
dementia
is a general term for symptoms including loss of thoughts and reason,
mental imbecility, idiocy while Alzheimer's disease is a progressive
form of presenile dementia that usually starts in the 40s to 50s, first
symptoms are impaired memory loss which is followed by impaired thoughts
and speech and finally complete helplessness.
Lets improve caring for our old ones!
refernce
- https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.alz.org%2Falzheimers-dementia%2Fdifference-between-dementia-and-alzheimer-s&psig=AOvVaw3HCoLDMVrsvtz2_l1vOJ8U&ust=1611477629273000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=2ahUKEwicy8KO1LHuAhXH4YUKHcjcBQUQr4kDegUIARDVAQ
- @yazzyfresh2def via TikTok
FACTS
Key healthy diet facts
- A healthy diet helps to protect against malnutrition in all its forms, as well as noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), including such as diabetes, heart disease, stroke and cancer.
- Unhealthy diet and lack of physical activity are leading global risks to health.
- Healthy dietary practices start early in life – breastfeeding fosters healthy growth and improves cognitive development, and may have longer term health benefits such as reducing the risk of becoming overweight or obese and developing NCDs later in life.
- Energy intake (calories) should be in balance with energy expenditure. To avoid unhealthy weight gain, total fat should not exceed 30% of total energy intake (1, 2, 3). Intake of saturated fats should be less than 10% of total energy intake, and intake of trans-fats less than 1% of total energy intake, with a shift in fat consumption away from saturated fats and trans-fats to unsaturated fats (3), and towards the goal of eliminating industrially-produced trans-fats (4, 5, 6).
- Limiting intake of free sugars to less than 10% of total energy intake (2, 7) is part of a healthy diet. A further reduction to less than 5% of total energy intake is suggested for additional health benefits (7).
- Keeping salt intake to less than 5 g per day (equivalent to sodium intake of less than 2 g per day) helps to prevent hypertension, and reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke in the adult population (8).
- WHO Member States have agreed to reduce the global population’s intake of salt by 30% by 2025; they have also agreed to halt the rise in diabetes and obesity in adults and adolescents as well as in childhood overweight by 2025 (9, 10).
Overview
Consuming a healthy diet throughout the life-course helps to prevent malnutrition in all its forms as well as a range of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) and conditions. However, increased production of processed foods, rapid urbanization and changing lifestyles have led to a shift in dietary patterns. People are now consuming more foods high in energy, fats, free sugars and salt/sodium, and many people do not eat enough fruit, vegetables and other dietary fibre such as whole grains.
The exact make-up of a diversified, balanced and healthy diet will vary depending on individual characteristics (e.g. age, gender, lifestyle and degree of physical activity), cultural context, locally available foods and dietary customs. However, the basic principles of what constitutes a healthy diet remain the same.
For adults
A healthy diet includes the following:
- Fruit, vegetables, legumes (e.g. lentils and beans), nuts and whole grains (e.g. unprocessed maize, millet, oats, wheat and brown rice).
- At least 400 g (i.e. five portions) of fruit and vegetables per day (2), excluding potatoes, sweet potatoes, cassava and other starchy roots.
- Less than 10% of total energy intake from free sugars (2, 7), which is equivalent to 50 g (or about 12 level teaspoons) for a person of healthy body weight consuming about 2000 calories per day, but ideally is less than 5% of total energy intake for additional health benefits (7). Free sugars are all sugars added to foods or drinks by the manufacturer, cook or consumer, as well as sugars naturally present in honey, syrups, fruit juices and fruit juice concentrates.
- Less than 30% of total energy intake from fats (1, 2, 3). Unsaturated fats (found in fish, avocado and nuts, and in sunflower, soybean, canola and olive oils) are preferable to saturated fats (found in fatty meat, butter, palm and coconut oil, cream, cheese, ghee and lard) and trans-fats of all kinds, including both industrially-produced trans-fats (found in baked and fried foods, and pre-packaged snacks and foods, such as frozen pizza, pies, cookies, biscuits, wafers, and cooking oils and spreads) and ruminant trans-fats (found in meat and dairy foods from ruminant animals, such as cows, sheep, goats and camels). It is suggested that the intake of saturated fats be reduced to less than 10% of total energy intake and trans-fats to less than 1% of total energy intake (5). In particular, industrially-produced trans-fats are not part of a healthy diet and should be avoided (4, 6).
- Less than 5 g of salt (equivalent to about one teaspoon) per day (8). Salt should be iodized.
For infants and young children
In the first 2 years of a child’s life, optimal nutrition fosters healthy growth and improves cognitive development. It also reduces the risk of becoming overweight or obese and developing NCDs later in life.
Advice on a healthy diet for infants and children is similar to that for adults, but the following elements are also important:
- Infants should be breastfed exclusively during the first 6 months of life.
- Infants should be breastfed continuously until 2 years of age and beyond.
- From 6 months of age, breast milk should be complemented with a variety of adequate, safe and nutrient-dense foods. Salt and sugars should not be added to complementary foods.
Practical advice on maintaining a healthy diet
Fruit and vegetables
Eating at least 400 g, or five portions, of fruit and vegetables per day reduces the risk of NCDs (2) and helps to ensure an adequate daily intake of dietary fibre.
Fruit and vegetable intake can be improved by:
- always including vegetables in meals;
- eating fresh fruit and raw vegetables as snacks;
- eating fresh fruit and vegetables that are in season; and
- eating a variety of fruit and vegetables.
Fats
Reducing the amount of total fat intake to less than 30% of total energy intake helps to prevent unhealthy weight gain in the adult population (1, 2, 3). Also, the risk of developing NCDs is lowered by:
- reducing saturated fats to less than 10% of total energy intake;
- reducing trans-fats to less than 1% of total energy intake; and
- replacing both saturated fats and trans-fats with unsaturated fats (2, 3) – in particular, with polyunsaturated fats.
Fat intake, especially saturated fat and industrially-produced trans-fat intake, can be reduced by:
- steaming or boiling instead of frying when cooking;
- replacing butter, lard and ghee with oils rich in polyunsaturated fats, such as soybean, canola (rapeseed), corn, safflower and sunflower oils;
- eating reduced-fat dairy foods and lean meats, or trimming visible fat from meat; and
- limiting the consumption of baked and fried foods, and pre-packaged snacks and foods (e.g. doughnuts, cakes, pies, cookies, biscuits and wafers) that contain industrially-produced trans-fats.
Salt, sodium and potassium
Most people consume too much sodium through salt (corresponding to consuming an average of 9–12 g of salt per day) and not enough potassium (less than 3.5 g). High sodium intake and insufficient potassium intake contribute to high blood pressure, which in turn increases the risk of heart disease and stroke (8, 11).
Reducing salt intake to the recommended level of less than 5 g per day could prevent 1.7 million deaths each year (12).
People are often unaware of the amount of salt they consume. In many countries, most salt comes from processed foods (e.g. ready meals; processed meats such as bacon, ham and salami; cheese; and salty snacks) or from foods consumed frequently in large amounts (e.g. bread). Salt is also added to foods during cooking (e.g. bouillon, stock cubes, soy sauce and fish sauce) or at the point of consumption (e.g. table salt).
Salt intake can be reduced by:
- limiting the amount of salt and high-sodium condiments (e.g. soy sauce, fish sauce and bouillon) when cooking and preparing foods;
- not having salt or high-sodium sauces on the table;
- limiting the consumption of salty snacks; and
- choosing products with lower sodium content.
Some food manufacturers are reformulating recipes to reduce the sodium content of their products, and people should be encouraged to check nutrition labels to see how much sodium is in a product before purchasing or consuming it.
Potassium can mitigate the negative effects of elevated sodium consumption on blood pressure. Intake of potassium can be increased by consuming fresh fruit and vegetables.
Sugars
In both adults and children, the intake of free sugars should be reduced to less than 10% of total energy intake (2, 7). A reduction to less than 5% of total energy intake would provide additional health benefits (7).
Consuming free sugars increases the risk of dental caries (tooth decay). Excess calories from foods and drinks high in free sugars also contribute to unhealthy weight gain, which can lead to overweight and obesity. Recent evidence also shows that free sugars influence blood pressure and serum lipids, and suggests that a reduction in free sugars intake reduces risk factors for cardiovascular diseases (13).
Sugars intake can be reduced by:
- limiting the consumption of foods and drinks containing high amounts of sugars, such as sugary snacks, candies and sugar-sweetened beverages (i.e. all types of beverages containing free sugars – these include carbonated or non‐carbonated soft drinks, fruit or vegetable juices and drinks, liquid and powder concentrates, flavoured water, energy and sports drinks, ready‐to‐drink tea, ready‐to‐drink coffee and flavoured milk drinks); and
- eating fresh fruit and raw vegetables as snacks instead of sugary snacks.
How to promote healthy diets
Diet evolves over time, being influenced by many social and economic factors that interact in a complex manner to shape individual dietary patterns. These factors include income, food prices (which will affect the availability and affordability of healthy foods), individual preferences and beliefs, cultural traditions, and geographical and environmental aspects (including climate change). Therefore, promoting a healthy food environment – including food systems that promote a diversified, balanced and healthy diet – requires the involvement of multiple sectors and stakeholders, including government, and the public and private sectors.
Governments have a central role in creating a healthy food environment that enables people to adopt and maintain healthy dietary practices. Effective actions by policy-makers to create a healthy food environment include the following:
- Creating coherence in national policies and investment plans – including trade, food and agricultural policies – to promote a healthy diet and protect public health through:
- increasing incentives for producers and retailers to grow, use and sell fresh fruit and vegetables;
- reducing incentives for the food industry to continue or increase production of processed foods containing high levels of saturated fats, trans-fats, free sugars and salt/sodium;
- encouraging reformulation of food products to reduce the contents of saturated fats, trans-fats, free sugars and salt/sodium, with the goal of eliminating industrially-produced trans-fats;
- implementing the WHO recommendations on the marketing of foods and non-alcoholic beverages to children;
- establishing standards to foster healthy dietary practices through ensuring the availability of healthy, nutritious, safe and affordable foods in pre-schools, schools, other public institutions and the workplace;
- exploring regulatory and voluntary instruments (e.g. marketing regulations and nutrition labelling policies), and economic incentives or disincentives (e.g. taxation and subsidies) to promote a healthy diet; and
- encouraging transnational, national and local food services and catering outlets to improve the nutritional quality of their foods – ensuring the availability and affordability of healthy choices – and review portion sizes and pricing.
- Encouraging consumer demand for healthy foods and meals through:
- promoting consumer awareness of a healthy diet;
- developing school policies and programmes that encourage children to adopt and maintain a healthy diet;
- educating children, adolescents and adults about nutrition and healthy dietary practices;
- encouraging culinary skills, including in children through schools;
- supporting point-of-sale information, including through nutrition labelling that ensures accurate, standardized and comprehensible information on nutrient contents in foods (in line with the Codex Alimentarius Commission guidelines), with the addition of front-of-pack labelling to facilitate consumer understanding; and
- providing nutrition and dietary counselling at primary health-care facilities.
- Promoting appropriate infant and young child feeding practices through:
- implementing the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes and subsequent relevant World Health Assembly resolutions;
- implementing policies and practices to promote protection of working mothers; and
- promoting, protecting and supporting breastfeeding in health services and the community, including through the Baby-friendly Hospital Initiative.
WHO response
The “WHO Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health” (14) was adopted in 2004 by the Health Assembly. The strategy called on governments, WHO, international partners, the private sector and civil society to take action at global, regional and local levels to support healthy diets and physical activity.
In 2010, the Health Assembly endorsed a set of recommendations on the marketing of foods and non-alcoholic beverages to children (15). These recommendations guide countries in designing new policies and improving existing ones to reduce the impact on children of the marketing of foods and non-alcoholic beverages to children. WHO has also developed region-specific tools (such as regional nutrient profile models) that countries can use to implement the marketing recommendations.
In 2012, the Health Assembly adopted a “Comprehensive Implementation Plan on Maternal, Infant and Young Child Nutrition” and six global nutrition targets to be achieved by 2025, including the reduction of stunting, wasting and overweight in children, the improvement of breastfeeding, and the reduction of anaemia and low birthweight (9).
In 2013, the Health Assembly agreed to nine global voluntary targets for the prevention and control of NCDs. These targets include a halt to the rise in diabetes and obesity, and a 30% relative reduction in the intake of salt by 2025. The “Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases 2013–2020” (10) provides guidance and policy options for Member States, WHO and other United Nations agencies to achieve the targets.
With many countries now seeing a rapid rise in obesity among infants and children, in May 2014 WHO set up the Commission on Ending Childhood Obesity. In 2016, the Commission proposed a set of recommendations to successfully tackle childhood and adolescent obesity in different contexts around the world (16).
In November 2014, WHO organized, jointly with the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the Second International Conference on Nutrition (ICN2). ICN2 adopted the Rome Declaration on Nutrition (17), and the Framework for Action (18) which recommends a set of policy options and strategies to promote diversified, safe and healthy diets at all stages of life. WHO is helping countries to implement the commitments made at ICN2.
In May 2018, the Health Assembly approved the 13th General Programme of Work (GPW13), which will guide the work of WHO in 2019–2023 (19). Reduction of salt/sodium intake and elimination of industrially-produced trans-fats from the food supply are identified in GPW13 as part of WHO’s priority actions to achieve the aims of ensuring healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. To support Member States in taking necessary actions to eliminate industrially-produced trans-fats, WHO has developed a roadmap for countries (the REPLACE action package) to help accelerate actions (6).
Rference:
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/healthy-diet
- https://www.google.com/search?q=healthy+diet&client=firefox-b-d&sxsrf=ALeKk00eAurS13kOwG0zyOQ_60140TgNEw:1611389866077&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjRob-Ez7HuAhUGEBQKHYYZAdwQ_AUoAXoECBgQAw&biw=1366&bih=654






















